Event handling
Working with event handlers
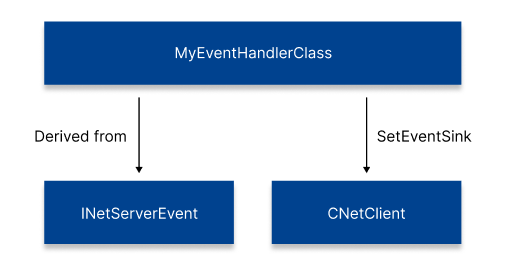
class MyEvent:public INetClientEvent
{
virtual void OnJoinServerComplete(...) override
{
// my event handler
...
}
}
MyEvent m_myEvent;
myNetServer->SetEventSink(&m_myEvent); myNetServer->OnJoinServerComplete = [...](...)
{
// my event handler
...
};myNetServer.OnJoinServerComplete = () =>
{
// my event handler
...
};
Last updated